Effectiveness and safety of starting insulin aspart premix therapy from different oral agents in routine clinical practice (#371)
Objective: To examine the effect of prior oral glucose-lowering drug (OGLD) therapy following 24 weeks of treatment with biphasic insulin aspart 30; subgroup analysis of data from insulin-naïve people with type 2 diabetes (T2DM) participating in the A1chieve study.
Methods: A1chieve was a non-interventional study evaluating the safety and clinical effectiveness of insulin analogues in people with T2DM (n=66,726) in routine clinical care in 28 countries across four continents.
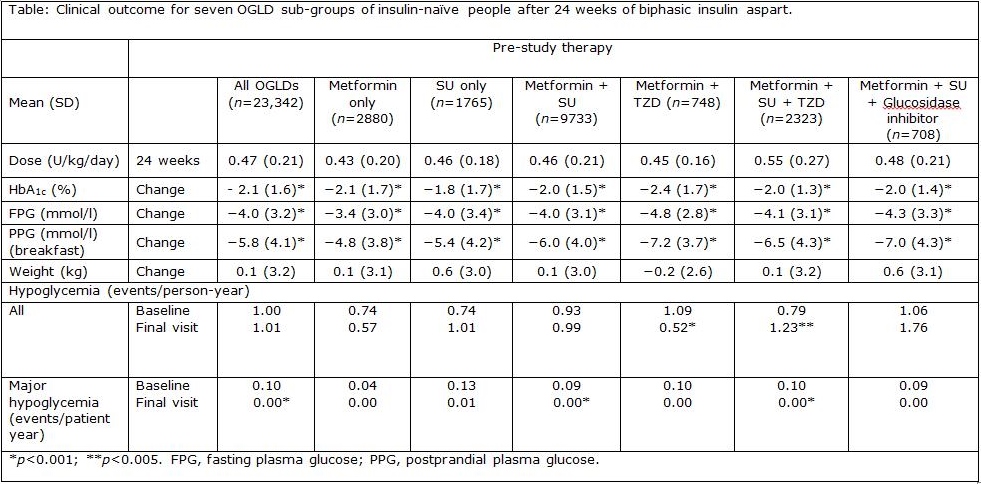
Results: Insulin dose by 24 weeks did not differ consistently by prior OGLD group (Table). Marked improvement in glycemic control (overall HbA1c −2.1 %) was found with all prior OGLDs and combinations thereof. This was also true for FPG and PPPG. The change in reported severe hypoglycemia was also similar between prior OGLDs, but change of overall hypoglycemia was erratic and inconsistent regionally, though with no change globally. There was no clinically significant change in body weight when starting aspart premix in any group (Table).
Conclusions: Starting insulin therapy with biphasic insulin aspart can be clinically successful independent of prior oral agent therapy.
Acknowledgments: Novo Nordisk